
Preview
Material for Exam 3 - Fall 2007
Print
the PDF version (no pictures, better printing)
Use the following chart and formulas when needed.
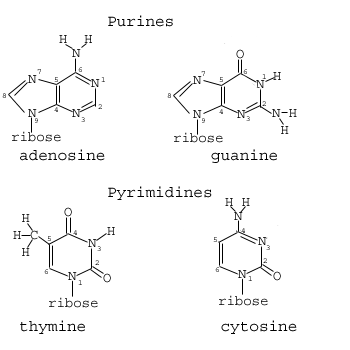
mRNA-Codon-to-Amino-Acid Decoder Chart |
|||||||||
|
|
2nd Letter |
|
||||||
1st Letter |
U |
|
C |
|
A |
|
G |
|
3rd Letter |
U |
UUU |
Phenylalanine |
UCU |
Serine |
UAU |
Tyrosine |
UGU |
Cysteine |
U |
C |
|||||||||
UUA |
Leucine |
UAA |
STOP |
UGA |
STOP |
A |
|||
UGG |
Tryptophan |
G |
|||||||
C |
CUU |
Leucine |
CCU |
Proline |
CAU |
Histidine |
CGU |
Arginine |
U |
C |
|||||||||
CAA |
Glutamine |
A |
|||||||
G |
|||||||||
A |
AUU |
Isoleucine |
ACU |
Threonine |
AAU |
Asparagine |
AGU |
Serine |
U |
C |
|||||||||
AAA |
Lysine |
AGA |
Arginine |
A |
|||||
AUG |
Methionine; START |
G |
|||||||
G |
GUU |
Valine |
GCU |
Alanine |
GAU |
Aspartate |
GGU |
Glycine |
U |
C |
|||||||||
GAA |
Glutamate |
A |
|||||||
G |
|||||||||
r=b-d G=rN G=rN(K-N)/K
 source
sourceHemophilia is a severe blood-clotting disorder that kills those afflicted before their reproductive years. The mutant allele for hemophilia is recessive and X-linked. Heterozygous (female) carriers do not manifest the disease. In 1894, Princess Alexandra, a carrier of hemophilia (and granddaughter of Queen Victoria), married the last Russian Czar, Nicholas II, a male without hemophilia.

In Arabian horses, there is a gene that controls whether or not a horse has pigments in its coat. For this trait, the allele that causes a lack of pigmentation in the hair is dominant (W) over the allele that allows the expression of color (w) controlled by other genes. Heterozygous (Ww) horses appear white regardless of other genes. Horses that receive two alleles for non-pigmentation (WW) suffer from the “lethal white gene” and do not survive long after birth. Homozygous recessive (ww) horses appear a certain color determine by other genes. For example, a black (EE) coat is known to be dominant over the chestnut (ee) color.
A breeder has a white (Ww) female that is impregnated by an unknown male. Immediately after the white offspring is born, she collects a sample of blood to determine the identity of the father (Horses have the same blood typing as people --A, B, o). The mother’s blood is genotype Ao, and the newborn’s blood is genotype AB.

Virally-caused influenza epidemics are commonly spread globally as super-epidemics known as pandemics. Flu viruses are usually spread from person-to-person by sneezing or coughing. Strains of flu often vary from one year to the next, thereby evading human immunity. Epidemics of cholera (caused by the Vibrio cholera bacterium), a dehydrating diarrheal disease, often occur following natural disasters such as floods or earthquakes that result in the deterioration of sanitation systems. Vibrio cholera is very debilitating because it secretes a toxin that binds to the lining of the intestine and triggers massive loss of ions and water from the patient’s bloodstream into the intestines. Public health officials often monitor sources of fecal-contaminated drinking water, such as wells and reservoirs, the most common means by which cholera infects people.
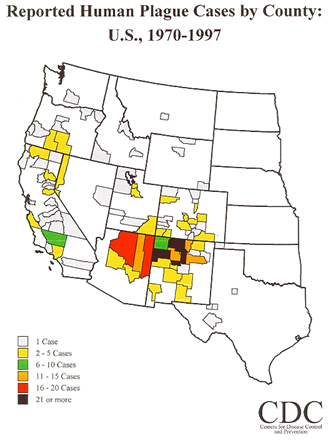
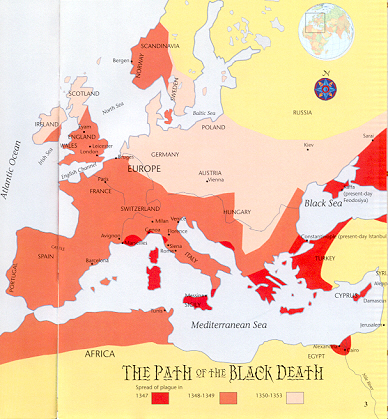
About 1347 A.D., plague swept Europe resulting in the death of 30%-50% of the population (in some cities even more). Nobility survived at higher rates than the “common” people. Plague bacteria, Yersinia pestis, are still found in rodents in highly rural areas of Arizona and New Mexico as a result of an infestation from Asia about 1900.
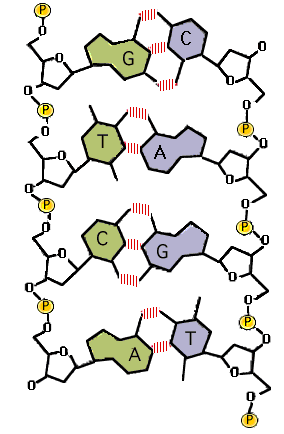
 source
source